Spanish version Versão em Português English Version
WHAT IS A CRO ?
Leia também:
- CROs para Pequenas Empresas: Qual o Melhor Modelo – FTE ou FFS?
- O Futuro das CROs: Como a Inteligência Artificial e a Automação Estão Revolucionando a Pesquisa Clínica
- O futuro dos CROs: aproveitando o poder da IA e da automação
- O Mercado de Serviços das Organizações de Pesquisa por Contrato (CRO): Panorama e Tendências
- O futuro dos CROs: aproveitando o poder da IA e da automação
- 2024 | Top 10 - CROs - Contract Research Organizations
- 2023 | Top 10 - CROs - Contract Research Organizations
- 2022 | Top 10 - CROs - Contract Research Organizations
- 2021 | Top 10 - CROs - Contract Research Organizations
- 2020 | Top 10 - CROs - Contract Research Organizations
- 2019 | Top 10 - CROs - Contract Research Organizations
- 2018 | Top 10 - CROs - Contract Research Organizations
- 2017 | Top 10 - CROs - Contract Research Organizations
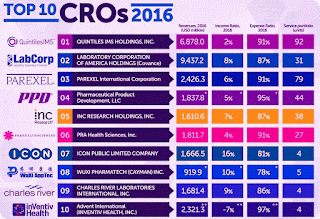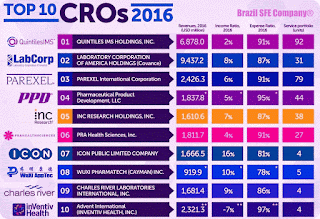
- 2016 | Top 10 - CROs - Contract Research Organizations
- 2015 | Top 10 - CROs - Contract Research Organizations
- 2014 | Top 10 - CROs - Contract Research Organizations
- 2013 | Top 10 - CROs - Contract Research Organizations
- 2012 | Top 7 - CROs - Contract Research Organizations
- 2011 | Top 10 - CROs - Contract Research Organizations
How do clinical trials work?
Once researchers have done initial testing on a promising treatment in a laboratory, they must begin a clinical trial to prove its safety and effectiveness before they are allowed to market it to the public. A CRO will conduct the trial in successive phases (Phase I, Phase II, and Phase III). The first step is to enroll clinical trial participants—who must meet certain criteria, depending on the intended patient profile of the specific trial—and who may be compensated for their time. As each phase of the study progresses, more is learned about a treatment’s effectiveness, risks, and side effects.
Contract Research Organization Roles and Responsibilities
A CRO is responsible for the planning, setup, execution, and day-to-day management of their contracted clinical trial. Handling and overseeing the technical side—data collection and medical testing—make up a significant portion of their duties. It is important to note that clinical compliance with regulatory agency guidelines is crucial, and adherence to Good Clinical Practice ( GCP ) standards is part of the CRO’s role , as they act as the central hub of the trial, connecting the sponsor with other stakeholders such as regulatory agencies, ethics committees, vendors, hospitals, etc.
What is a CRO in clinical trials?
In clinical trials, a CRO is the entity that plans, develops, and coordinates the clinical trial protocol. It then executes that protocol in accordance with regulatory agency rules and GCP standards. A sponsor—which may have many potential treatments it wants to test through a clinical trial—hire a CRO to handle the time-consuming and resource-intensive work required of a clinical trial. The sponsor is able to leverage the CRO’s expertise, which, because of the CRO’s repeated execution of trial after trial, is able to anticipate potential delays and pitfalls and avoid them in advance.
What does a contract research organization do?
CROs are able to provide a wide range of clinical research services to medical sponsors, including but not limited to :
- Project and Data Management
- Supervision and execution of clinical studies
- Research and Compliance Education
- Drug and Disease Coding
- Validation Programming
- Product Development and Commercialization Planning
- Safety and efficacy report
- Quality Analysis
- Biostatistical analysis
- Statistical Analysis
- Medical Writing
Types of Contract Research Organizations
Different CROs may offer varying services, but they are most commonly grouped by where their contribution falls within the sponsor's research agenda, along with the CRO's primary function :
- Discovery
- Preclinical
- Clinical
- Laboratory Services
Frequently Asked Questions:
Who is the sponsor of clinical research?
The sponsor is the organization that initiates a clinical trial to investigate the safety and effectiveness of a potential treatment. The sponsor partners with a CRO, and the CRO manages and runs the sponsor's clinical trial.
What is a CRO company?
A CRO is an organization that offers its services to pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and medical device companies to assist them in various forms of research. Some CROs are specifically focused on working with sponsoring companies of a certain size. For example, Synteract focuses on the SMID market , or small- to medium-sized biopharmaceutical companies.
What is the difference between a CRO and a pharmaceutical company?
Pharmaceutical companies develop drug treatment candidates for eventual commercialization. Once that treatment is ready to be tested in a clinical trial setting in order to prove to regulatory authorities that it is safe and effective, a pharmaceutical company will partner with a CRO. The CRO will then plan, coordinate, and execute the clinical trial.
Benefits of Contract Research Organizations
The main benefit of CROs is that they allow sponsors to do what they do best—focus on treatment development—while CROs handle the nuts and bolts of clinical trial planning and execution. Given the extensive resources and processes required to conduct a clinical trial safely and efficiently—including data collection, project management, and day-to-day patient care—delegating these functions to a CRO that already has these systems in place is an attractive solution for many sponsors.
What is the role of a contract research organization?
A CRO acts on behalf of a sponsor and is responsible for ensuring that their clinical trial runs smoothly. A CRO replaces what would otherwise be an expensive, intermittently needed in-house team. Managing and executing all clinical trial functions—especially for those sponsors who rarely need to conduct clinical trials—would be cost and resource prohibitive.
What metrics should contract research organizations use?
CROs employ different metrics to measure effectiveness and progress, depending on the goals and expectations of sponsors and the constraints of GPC and regulatory frameworks. There are three basic timelines that deserve attention and evaluation:
- Sponsor's draft budget received for finalized budget
- IRB sent to IRB approved
- Full execution of the contract for open registration
What is an early-stage contract research organization?
Clinical trials occur in phases, usually Phase I , Phase II , and Phase III . If a drug does not meet safety or efficacy milestones at any point in these successive phases, it cannot proceed to the next phase. An early-stage CRO focuses on the early-stage phases (mostly Phase I , sometimes Phase II ).
How to choose a CRO?
A CRO must be able to provide the right combination of experience, expertise, communication and responsiveness. Understanding your therapeutic area and what to expect from your study phase is key. Transparency is also important – being able to resolve potential issues early in the process, collaboratively, can mean the difference between successful milestones and unnecessary delays.
Choosing a CRO is one of the most important decisions a sponsor can make when preparing to initiate a clinical trial. Understanding the role and function of a CRO, understanding the factors to consider when choosing a CRO, and knowing what to realistically expect from the CRO you choose all need to be taken into consideration.
👉 Don't forget to follow André Bernardes on Linkedin or subscribe to our newsletter 🔔 to be notified about all posts. Click here and contact me via What's App.
















Nenhum comentário:
Postar um comentário
Compartilhe sua opinião e ponto de vista: